Harvard endowment management plays a crucial role in shaping Harvard University finances, controlling how funds are allocated across various needs, including financial aid funding and long-term budgeting. With an endowment currently valued at a staggering $53 billion, the responsibility of overseeing this vast wealth rests with the Harvard Management Company. However, the complexity arises from the extensive restrictions imposed by donors, which often limit the flexibility of these funds. Less than 5% of the endowment is unrestricted, leaving university leadership to navigate through tight budget constraints when planning for future initiatives. Consequently, effective university budget management is vital, as it allows Harvard to maintain its commitment to education while adapting to both immediate financial needs and long-term stability.
The stewardship of Harvard’s financial resources, often referred to as endowment oversight, is pivotal in influencing the fiscal health of Harvard University. The impressive endowment, which amounts to billions, serves as a financial backbone for various operations including educational programs and student support services. However, this extensive wealth is frequently restricted, complicating decisions surrounding funding allocation and usage. To ensure sustainable operations amid fluctuating market conditions, strategic financial planning becomes essential for the university. As educational institutions continuously face pressures for financial aid and budgeting, adept management of these significant assets forms the foundation for Harvard’s ongoing success.
Understanding the Structure of Harvard’s Endowment Management
Harvard University’s endowment management plays a crucial role in its financial stability and budgetary flexibility. With an endowment valued at a staggering $53 billion, it is imperative to understand how much of that funding is available for immediate University needs. The reality is that a significant portion of this endowment is restricted due to donor stipulations, meaning that funds are earmarked for specific purposes and cannot be used for general operational costs. This situation presents a dual-edged sword for Harvard: while the endowment provides a financial safety net, its restrictions limit how effectively it can be applied to address the University’s pressing financial aid and operational needs.
The distribution of the endowment across Harvard’s various Schools further complicates its management. Less than 5% of the endowment is unrestricted, which means University leadership has limited flexibility in reallocating funds at their discretion. This is particularly critical during fiscal downturns or in response to external funding issues, such as federal research grants being put on hold. Understanding these restrictions allows stakeholders to appreciate the financial constraints under which the administration operates, emphasizing the importance of strategic long-term budgeting.
Navigating Financial Aid Funding Through Endowment Resources
Financial aid funding is a predominant use of Harvard’s endowment, enabling the University to maintain an accessible and diverse student body. Approximately 20% of the annual distribution from the endowment is allocated toward financial aid, significantly reducing barriers for students from varied socio-economic backgrounds. However, this considerable commitment to financial aid also shapes the University’s fiscal landscape, requiring careful management to ensure that current spending does not impede future operational capacities.
The increasing financial aid commitments place an ongoing burden on the endowment, which may require adjustments to the payout strategy or even borrowing against the endowment for immediate needs. While these actions can temporarily alleviate financial pressures, they create long-term implications for budget sustainability. Therefore, Harvard’s administration must balance the dual objectives of supporting students through generous financial aid while also ensuring that the endowment retains sufficient capital to fund future educational and operational needs.
The Impact of Economic Factors on Harvard’s Budget Management
Harvard’s endowment management cannot be divorced from the broader economic context in which it operates. Macroeconomic conditions such as inflation, market volatility, and crises can dramatically impact endowment performance and, by extension, the University’s budget management strategies. For instance, periods of economic downturn, as seen during the 2008 financial crisis, have led to substantial losses in endowment value, bluntly affecting financial decision-making processes. Universities like Harvard must therefore prepare for these fluctuations, implementing flexible budgeting practices that can adapt to changing economic landscapes.
In light of recent threats to funding, such as potential changes in federal tax status or the freezing of research grants, the University faces a precarious balancing act. leaders need to engage in thorough scenario analyses, considering various possible futures that could alter revenue streams and necessitate adjustments in spending policies. These proactive measures can help stave off financial crises and prepare the University for robust, long-term financial health.
Strategic Planning in University Budget Management
Strategic planning is a fundamental aspect of Harvard’s approach to budget management, particularly in relation to its sizable endowment. By analyzing current financial conditions and projecting future scenarios, the University can establish a framework that balances immediate fiscal needs with the overarching goal of long-term sustainability. This is critical in an environment where both funding sources and operational costs are subject to unpredictable changes. For example, economic recessions necessitate budget cuts that can affect staffing and programs if not planned for in advance.
Moreover, the integration of long-term budgeting practices into the University’s financial strategy ensures that decisions made in response to short-term needs do not compromise future resources. Strategic approaches may include setting firm priorities for fund allocations and regularly revisiting these strategies to ensure alignment with the evolving financial landscape. Such planning not only promotes fiscal health but also reinforces the University’s commitment to maintaining its educational goals and responsibilities.
Long-Term Financial Planning: Lessons from Harvard’s Endowment
Harvard’s experience in long-term financial planning reveals valuable insights into effective endowment management, showcasing the necessity of foresight and adaptability. One key lesson is the importance of not simply focusing on immediate cash flow needs but also considering how current spending decisions will influence future financial health. In light of this, Harvard has often adopted a ‘smoothing’ strategy, wherein they modulate spending rates in good years to preserve capital for leaner periods.
Additionally, planning for the future involves a rigorous examination of investment projections and guessing potential market trends. By maintaining conservative estimates for contributions and expenditures, Harvard operates with a buffer against unexpected downturns. The success of the endowment management over the years is a testament to the effectiveness of strategic long-term financial planning, ensuring that the University remains resilient in the face of economic uncertainties.
The Role of Harvard’s Management Company in Endowment Oversight
The Harvard Management Company plays a vital role in overseeing the University’s endowment, ensuring that investments are managed effectively to generate sustainable returns. This entity is tasked with not only growing the endowment through prudent investment choices but also adhering to the restrictions set by donors. The complex fiduciary responsibilities require a careful understanding of both market dynamics and institutional priorities to safeguard the institution’s financial future.
The management company’s strategies are designed to align with Harvard’s overall financial goals, balancing risk and reward to maximize growth while considering the unique constraints of the endowment’s structure. Their decisions directly influence how effectively the University can manage its financial aid funding, operational costs, and long-term budgeting initiatives, ultimately shaping the overall financial landscape of Harvard University.
Addressing Exogenous Shocks in University Financing
Exogenous shocks, such as economic downturns or shifts in government policy, pose significant risks to Harvard’s endowment and require timely responses from the administration to mitigate impacts on the University’s finances. In challenging times, Harvard has had to employ various strategies, including adjusting payout rates from the endowment or temporarily increasing the spending allowance. Such measures can provide immediate relief but may also create long-term financial burdens.
Anticipating these external challenges necessitates robust risk management strategies that can prepare Harvard for a range of scenarios. By integrating scenario planning into their financial strategy, University leaders can develop contingency plans that help maintain operational continuity despite fluctuating funding availability. This proactive approach is essential to ensure that the institution can navigate unforeseen financial hurdles without compromising its long-term goals.
The Importance of Responsive Budget Strategies
Responsive budgeting strategies are critical for university financial management, particularly at institutions like Harvard, where the endowment serves as a backbone for multiple financial needs. By having flexible spending plans that can adapt to changes in funding availability, administrators can ensure that the University responds swiftly to new financial realities. This might involve reassessing budget priorities or reallocating resources to address immediate operational needs while still maintaining funding for essential programs.
Implementing responsive budget strategies allows Harvard to align its financial resources effectively with institutional priorities. By ensuring that spending is both strategic and adaptable, the University can maintain its commitment to its mission even in times of financial stress. This approach emphasizes the importance of being prepared for shifts in both internal and external funding sources and highlights how proactive financial management can safeguard the institution’s long-term success.
Future Challenges in Endowment Management at Harvard
Looking forward, Harvard faces several potential challenges in managing its endowment effectively. Changes in federal funding policies, shifts in donor behavior, and the unpredictability of market conditions could all disrupt traditional funding mechanisms. University leaders may need to innovate continuously to find new revenue streams or adjust financial aid policies while keeping the endowment’s restrictions in mind.
Moreover, as the landscape of higher education evolves, so too will the expectations placed upon Harvard’s financial resources. Emphasizing transparency and responsible management will be crucial in navigating these challenges. If the University can ensure that it meets its financial commitments while adhering to the philanthropic wishes of its donors, it can maintain the trust of both the community and the broader public.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of Harvard University finances in endowment management?
Harvard University finances are crucial in managing the endowment, which supports various academic programs, financial aid, and operational costs. The endowment allows the University to maintain financial flexibility while adhering to donor restrictions and ensuring long-term stability.
How do endowment restrictions impact Harvard’s budget management?
Endowment restrictions limit how funds can be utilized, often designating them for specific schools or purposes. This can impact Harvard’s budget management by constraining available resources for unforeseen expenses, requiring careful planning and prioritization.
How does Harvard’s endowment support financial aid funding?
A significant portion of Harvard’s endowment directly contributes to financial aid funding. This allocation helps the University maintain its commitment to providing generous financial support, reducing the financial burden on students and families.
What is the importance of long-term budgeting in Harvard endowment management?
Long-term budgeting is essential in Harvard’s endowment management to balance immediate financial needs with future stability. It helps the University project spending and investment returns, ensuring that funds are available for future commitments while managing current expenditures wisely.
What are the challenges faced in Harvard’s university budget management?
Harvard’s university budget management faces challenges such as donor restrictions, fluctuating investment returns, and the need for financial aid funding. These factors can complicate resource allocation and necessitate strategic planning to address both current and future needs.
How does Harvard ensure effective endowment management amidst economic uncertainties?
Harvard employs strategic long-term budgeting and diversification of investments to manage its endowment effectively. By smooting distributions and adhering to financial projections, the University can navigate economic uncertainties while preserving fund integrity for future expenditures.
What measures does Harvard take to alleviate financial uncertainty using its endowment?
To alleviate financial uncertainty, Harvard may increase distributions from the endowment during crisis situations, such as economic downturns. However, such measures are undertaken cautiously, as they can impact future resource availability.
How does Harvard’s endowment management respond to potential federal funding risks?
In response to potential federal funding risks, Harvard’s endowment management may conduct scenario analyses to assess impacts on revenue. This proactive approach allows the University to strategize and adjust budgeting practices accordingly to maintain financial health.
What is the relationship between Harvard’s endowment and its long-term financial planning?
The relationship between Harvard’s endowment and long-term financial planning is interconnected; effective endowment management provides the financial resources necessary to support the University’s strategic goals, sustainability, and future initiatives while balancing current operational needs.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Harvard’s Endowment Value | As of the beginning of the fiscal year, Harvard’s endowment is valued at a record $53 billion. |
| Restrictions on Funds | Most of the endowment funds are donor-restricted and primarily allocated to specific schools, limiting flexibility. Only about 5% is unrestricted. |
| Impact of Recent Political Conflicts | The Trump administration’s freezing of research grants and threats to change Harvard’s tax-exempt status poses risks to funding. |
| Usage of Endowment | Endowment funds are often used to cover budget deficits, financial aid, and operational costs, creating a cycle of dependency. |
| Strategies for Financial Stability | Harvard can adopt strategies like adjusting the payout rate, borrowing against the endowment, or using funds for current expenses in emergencies. |
| Long-term Planning vs. Immediate Needs | Harvard’s approach to endowment management emphasizes balancing immediate financial needs with long-term sustainability. |
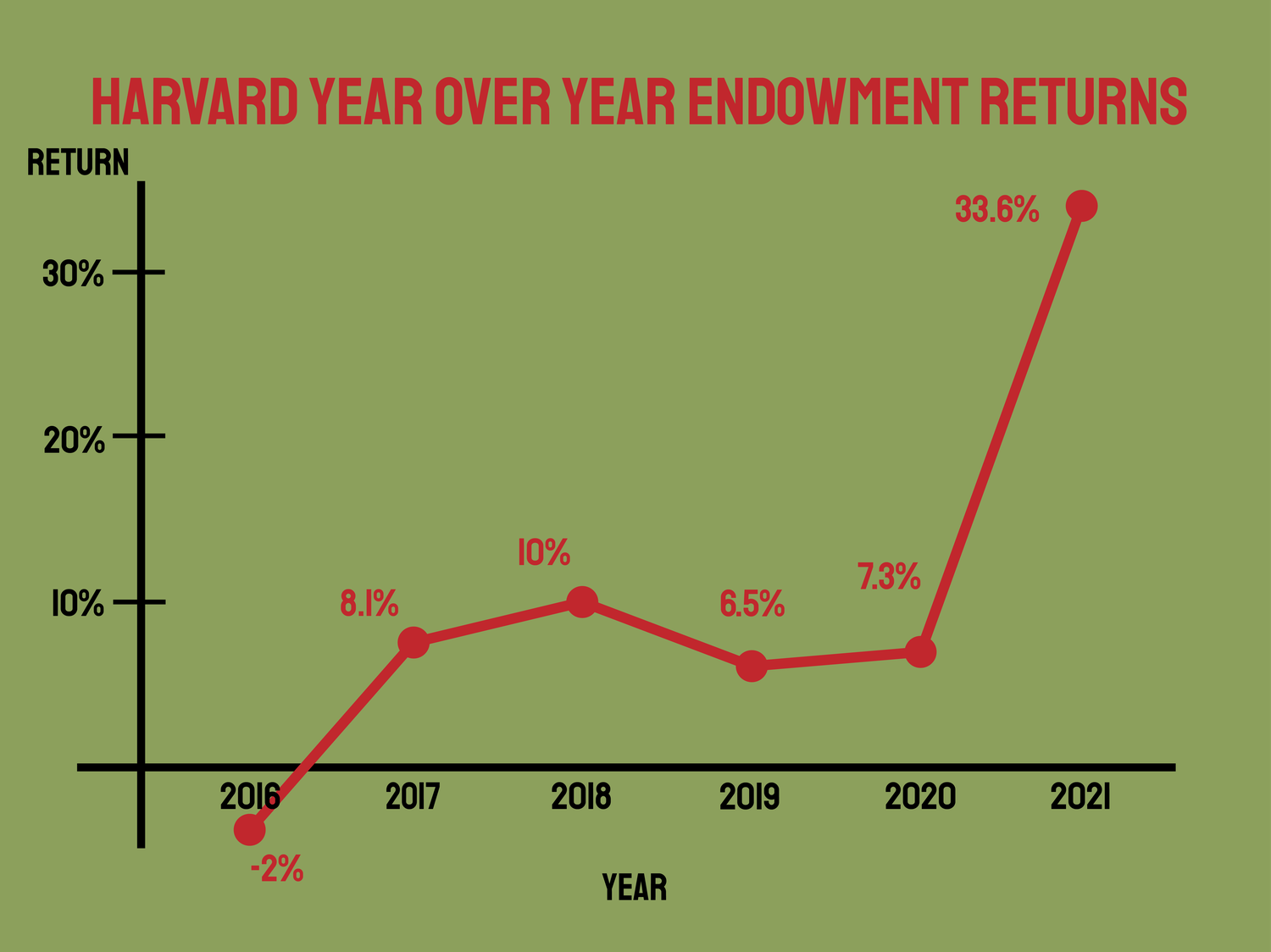
| Market Volatility | Historical data shows the endowment’s value can fluctuate significantly, necessitating careful management and scenario analyses. |
| Future Implications | University leaders must prepare for potential long-term changes in funding sources and adjust spending or revenue accordingly. |
Summary
Harvard endowment management is a complex balancing act that requires careful consideration of both immediate financial needs and the long-term implications of funding decisions. As the University grapples with unprecedented challenges and a newly volatile political and economic landscape, it is essential for leadership to strategize effectively to safeguard the future of its endowment. Understanding the inherent risks and restrictions associated with Harvard’s substantial endowment will be critical in navigating these uncertainties.